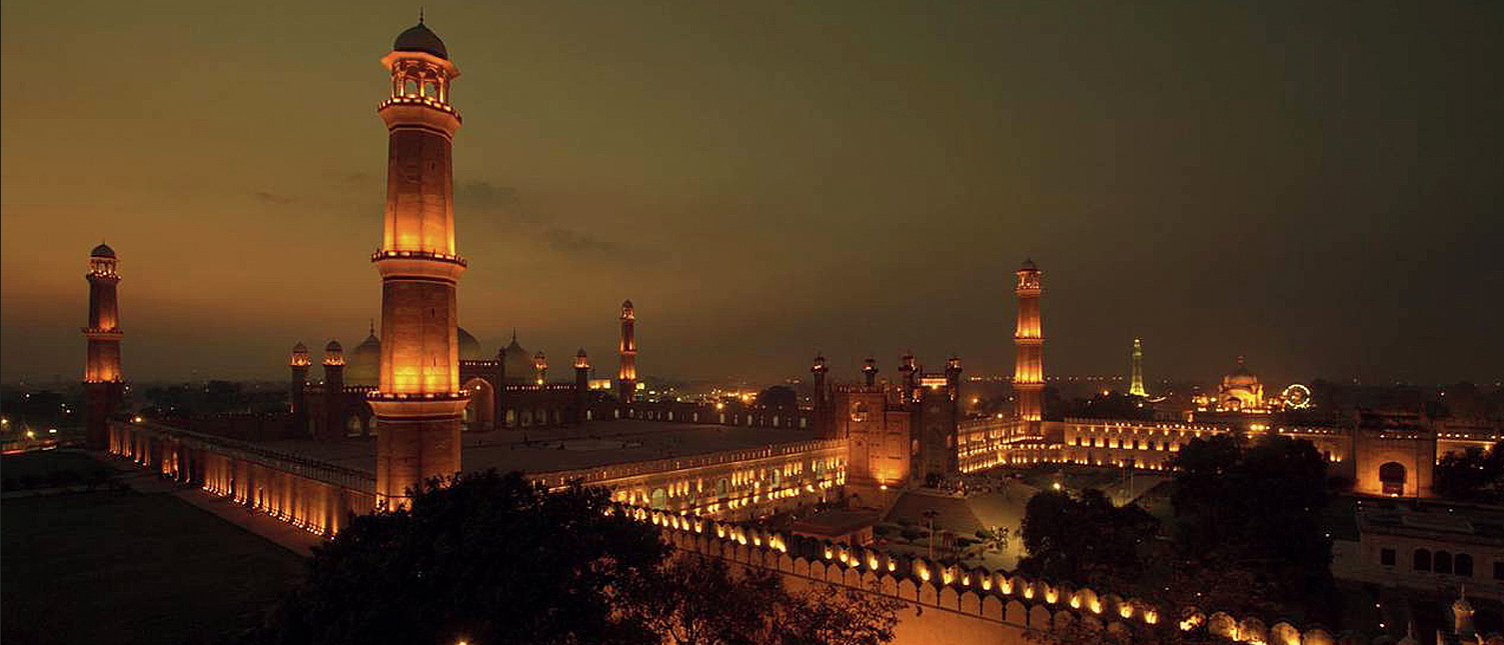
Why Pakistan’s urban glow is hiding our stars and what we can do about it? On a moonless night in rural Pakistan, the sky once offered a breathtaking panorama of
Astroncia enters NASA Space Apps Karachi 2025 as Tech Partner — bringing with it a vision that extends far beyond the traditional scope of a hackathon. While Space Apps gathers
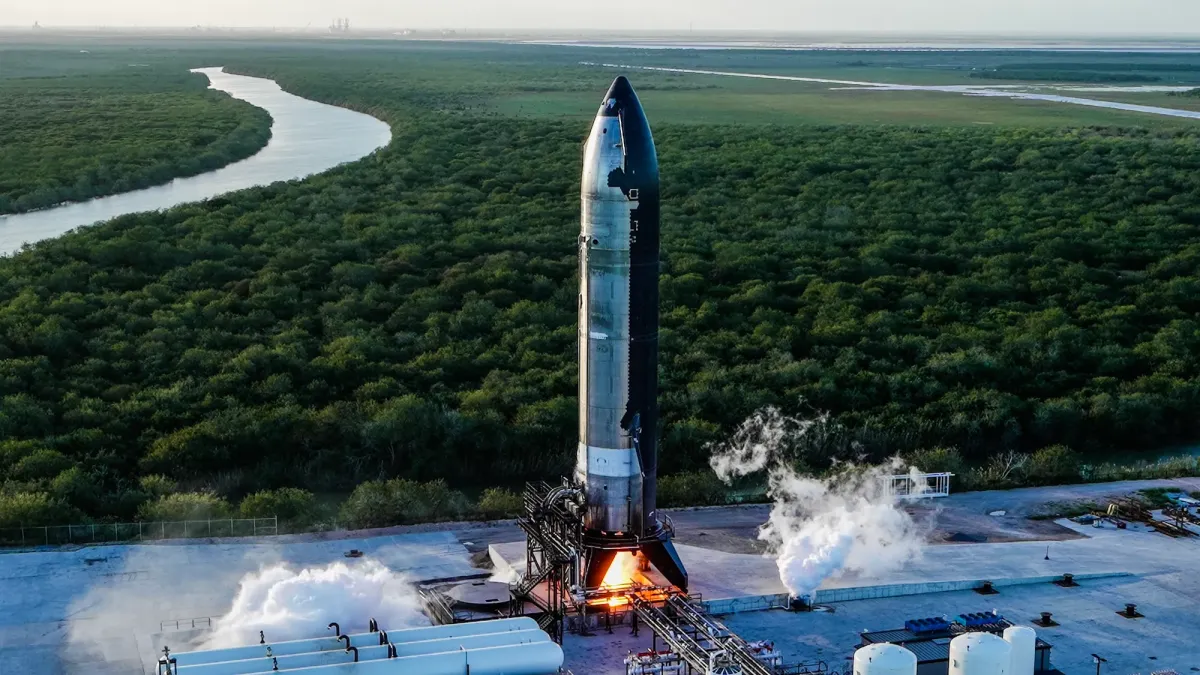
Space exploration has always represented humanity’s quest for discovery and the advancement of engineering. Among modern innovations, SpaceX’s Starship is a groundbreaking spacecraft designed to push the boundaries of space
When Albert Einstein first proposed the existence of gravitational waves in 1916 as part of his general theory of relativity, the concept seemed more like science fiction than reality (Einstein, 1916). These ripples in spacetime, caused by some of the universe's most violent and energetic processes, eluded direct observation for nearly a century. However, the groundbreaking detection of gravitational waves by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in 2015 marked the dawn of a new era in astronomy, allowing us to observe the cosmos in ways previously unimaginable.
The story of our universe begins with an event so monumental that it redefined our understanding of existence: the Big Bang. Approximately 13.8 billion years ago, the cosmos as we
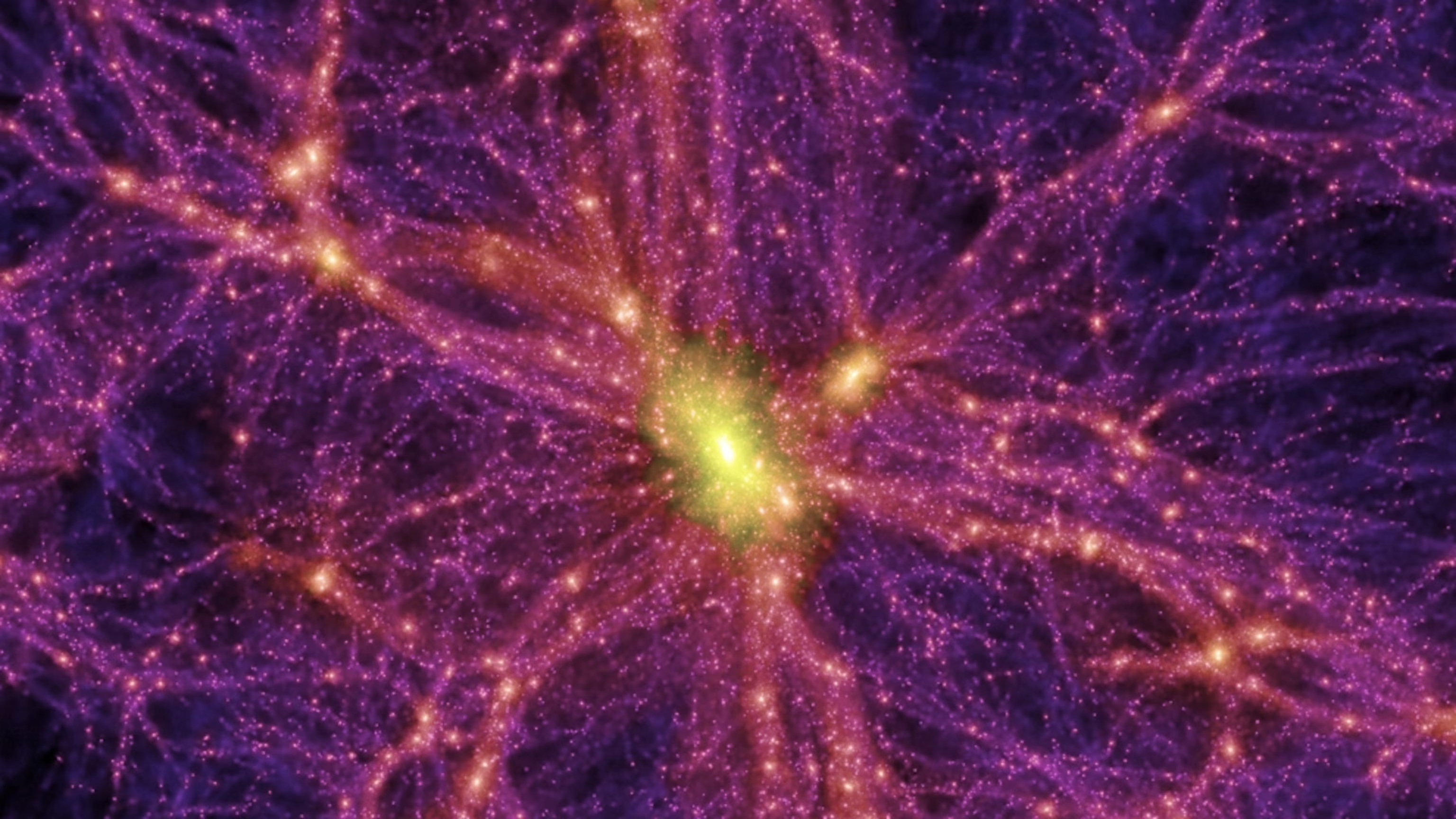
In the vast expanse of the universe, a mysterious form of matter exerts a powerful influence, yet it remains invisible to our eyes and instruments. Known as dark matter, this elusive substance does not emit, absorb, or reflect light, making it undetectable through conventional means. However, its gravitational pull shapes galaxies, bends light, and governs the formation of cosmic structures. Scientists estimate that dark matter comprises approximately 27% of the universe’s total mass-energy content, dwarfing the 5% that is visible matter (Planck Collaboration, 2020). Despite its elusive nature, dark matter is a central focus in astrophysics, as understanding it could unlock profound secrets about the cosmos.
Space technology continues to evolve, transforming how humans communicate, explore, and understand the universe. One of the most impactful advancements in recent years is the rise of satellite mega-constellations. These
Spacecraft reentry into Earth’s atmosphere is one of the most perilous phases of any space mission. Temperatures can exceed 1,650°C (3,000°F) due to the intense friction between the spacecraft and
The vast expanse of space presents a unique challenge for spacecraft navigation. Without roads, landmarks, or atmospheric reference points, determining a satellite’s precise position and orientation requires innovative engineering solutions.
In 1990, as the Voyager 1 spacecraft prepared to leave the confines of our solar system, a simple yet profound command was sent to the probe. Scientists at NASA, led